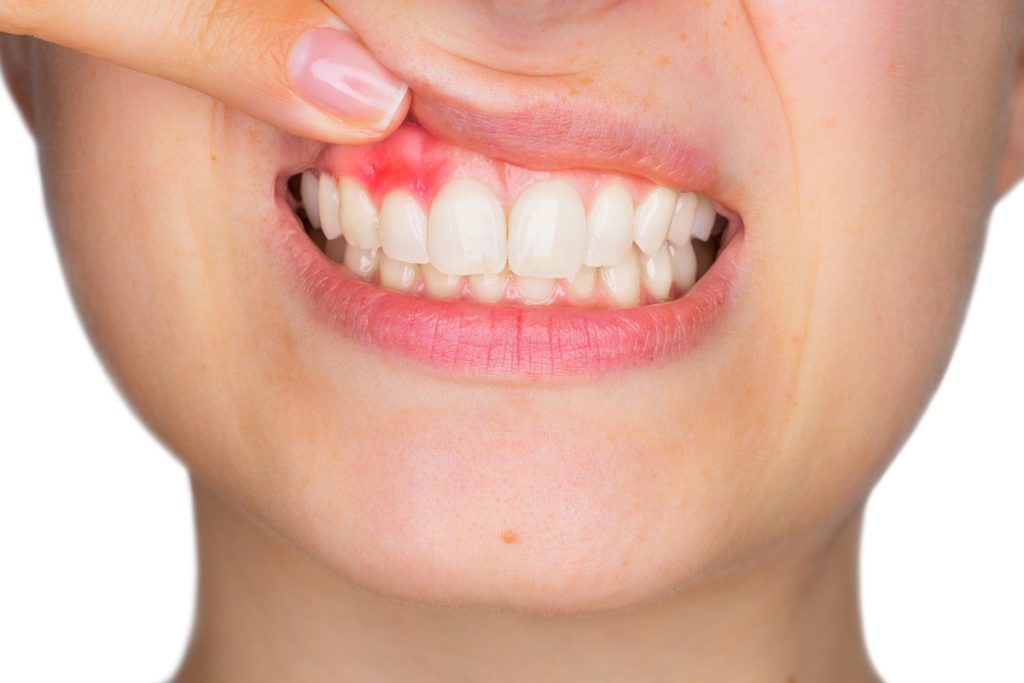
What types of gum diseases exist?
Your dentist in Sydney CBD knows that many people focus more on their teeth more than their gums when it comes to the maintenance of appropriate oral health. Teeth are very important, but the gums are at least as important for oral health as teeth. Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are a group of diseases that affect the tissue that surrounds the teeth and keeps them fixed. Periodontal diseases usually start with the overgrowth of bacteria. These bacteria constitute the healthy microflora of the oral cavity. However if their presence exceeds a healthy amount, they can often be the cause of various diseases, and if left untreated they can cause severe issues, such as tooth loss.
Gingivitis, the inflammation of the gingiva (gum) mostly appears prior to periodontitis. If gingivitis is left untreated it can progress into periodontitis, which is a more serious issue. It is an important note that not all cases of gingivitis continue to progress into periodontitis. The simplified pathogenesis of gingivitis is the following: the oral bacteria over accumulate, which induces an immune response. The innate immune response is not specific, which results in the inflammation of the gum (gingiva). This often does not eliminate the bacteria, which can result in the chronic inflammation of the gum tissue. At this stage the teeth are still strongly attached. This means that the process at this point is reversible.
If gingivitis is left without treatment it can progress into a disease called periodontitis. In this condition the innermost part of the gum tissue and the jawbone get pulled away from the teeth, creating a small space between them, which allows the accumulation of food debris and subsequent infection. This is followed by inflammation, which is one of the results of the immune response to the food debris and the infections. Toxins produced by the bacteria may start degrading the bone and the other tissues that keep the tooth in their place. With the progression of the disease the tooth slowly becomes more and more loose, leading to eventual tooth loss. Gum disease is one of the main causes of tooth loss in adults.
What can cause gum diseases?

One of the primary causes of gum disease is poor oral hygiene. This allows for the accumulation and overgrowth of bacteria, which can result in the initiation of gum disease as described above. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to the pathogenesis of gum disease, as these habits can impair the gum tissue’s natural self-repair mechanisms, resulting in its eventual degradation. Certain hormonal changes induced by e.g. pregnancy, menopause, puberty or even menstruation can make the gums become sensitive, which promotes gingivitis. Diseases that affect the immune system can also contribute to gum diseases: HIV, cancer and diabetes have been associated with an increased incidence of gum diseases due to the increased susceptibility to infectious microorganisms.
How to prevent gum diseases?
The first step to preventing gum diseases is the maintenance of the necessary oral hygiene. When brushing your teeth, make sure you clean your gums as well, and use a mouthwash to prevent the bacteria from overgrowth.
Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risks. Before proceeding you should seek a second
opinion from an appropriately qualified health practitioner.